
- #Not enough memory to open this page in chrome drivers
- #Not enough memory to open this page in chrome free
- #Not enough memory to open this page in chrome windows
A contiguous region divided into 4kb physical pages.

A contiguous region divided into 4kb virtual pages.
#Not enough memory to open this page in chrome windows
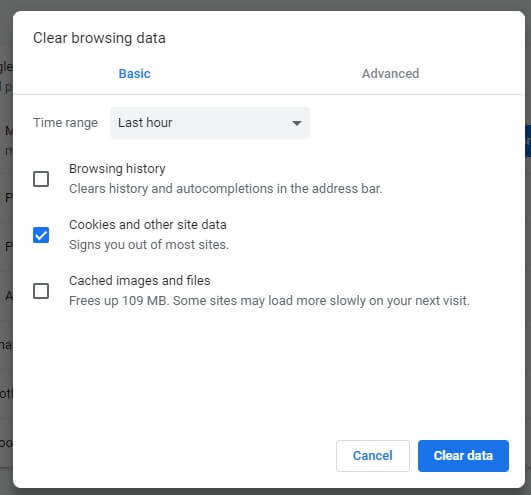
Not being aware of this difference can cause architecture choices that have a larger than expected resource impact on Windows and incorrect interpretation for metrics on Windows In Unix variants, usage usually only consumes system resources when pages are touched. Pragmatically this means that in Windows, malloc(10*1024*1024*1024) will immediately prevent other applications from being able to successfully allocate memory thereby causing them to crash or not be able to open. Key gotchas Windows allocation uses resources immediately other OSes use it on first touch.Īrguably the biggest difference for Windows and other OSes is memory granted to a process is always “committed” on allocation. The goal of this document is to give a common set of vocabulary and concepts such that Chromium developers can more discuss questions like the ones above without misunderstanding each other. However, even in macOS, Android, CrOS, and “standard desktop linux” each also have enough divergences (compressed memory, pagefile vs swap partition vs no swap, overcommit settings, memory perssure signals etc) that even answering “how much memory is Chromium using” is hard to do in a uniform manner.
#Not enough memory to open this page in chrome free
For example, it is impossible to return all resources (physical ram as well as swap space) to the OS in a way brings them back on demand which drastically changes the way one can handle free lists. There is at least one major schism between Windows-based machines and more unixy systems. In many of the above, the answer actually changes per operating system variant.
#Not enough memory to open this page in chrome drivers
You work on a multi-process browser implementing the web platform with high security guarantees.
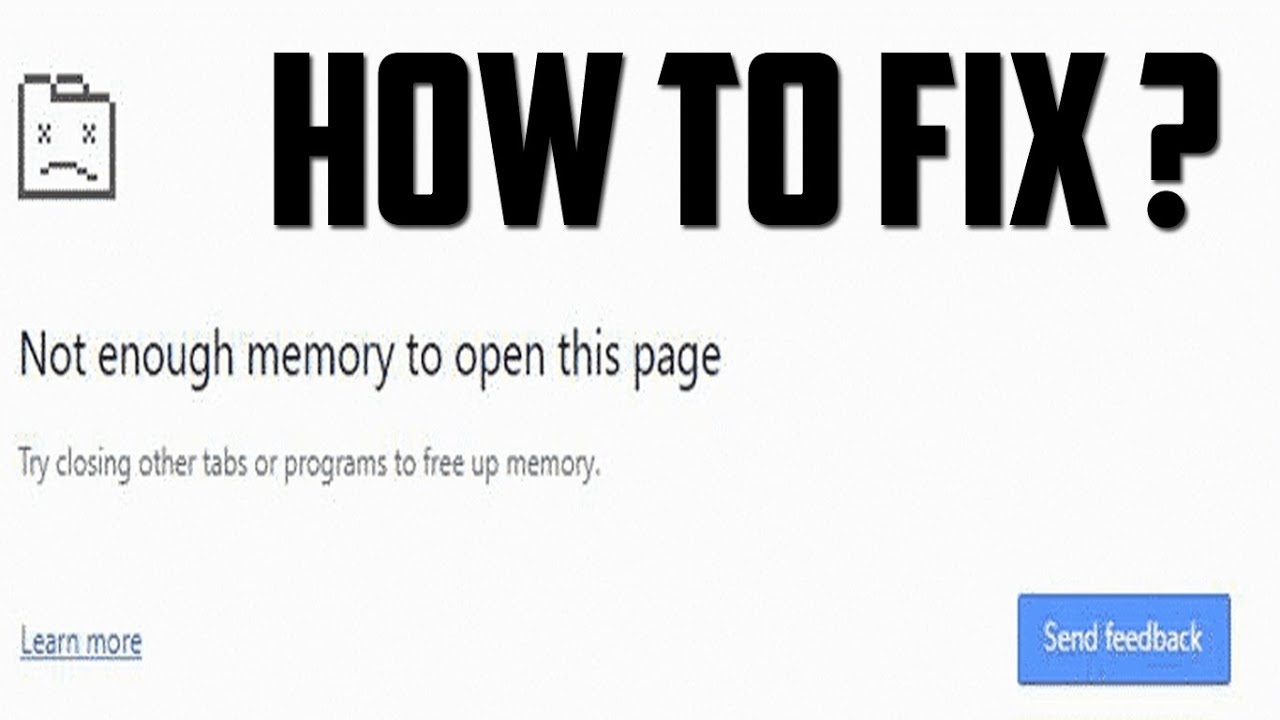
Yes, this is complicated stuff.but don't despair. Unfortunately, the distinctions end up being very relevant when working near out of memory conditions or analyzing overall performance when there is any amount of memory pressure this makes crafting and interpreting memory statistics hard.įortunately, the point of this doc is to give succinct background that will help you ramp up on the subtleties to work in this space. There are lots of differences and subtleties that change per operating system and even per operating system configuration.įortunately, these differences mostly disappear when a program is running with sufficient resources. Key Concepts in Chrome Memory What‘s so hard about memory? Isn’t it just malloc and free?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
